面试相关 图的最短路径问题
题目:图的最短路径问题
求解双子峰到金门大桥的最短路径(可认为两点之间的距离都为1)。
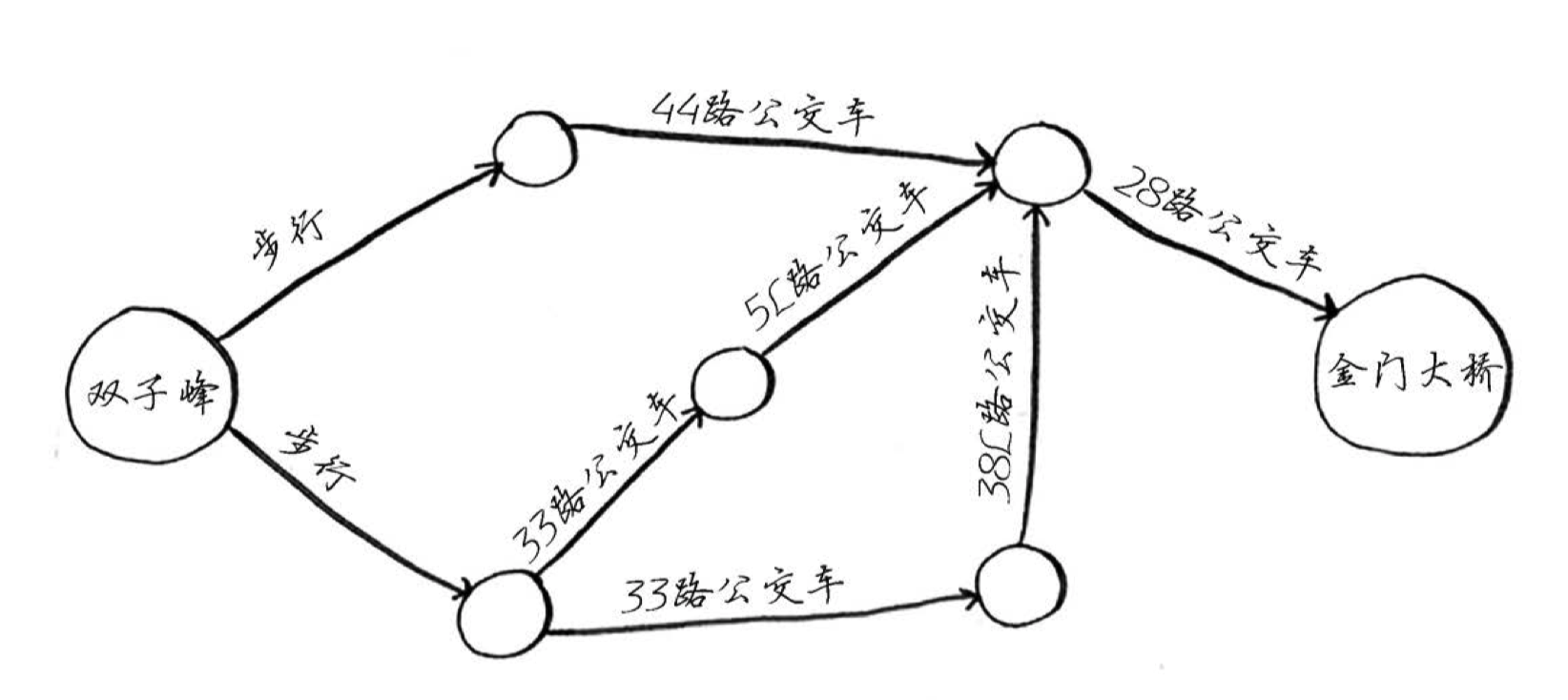
根据题目分析,构建出邻接表:
1 | // 代表无穷大,当两点之间没有直接可达路径时,两点距离为无穷大 |
方法一:动态规划
思路:动态规划,状态转移方程为:shortDistance[j] = min(shortDistance[j], shortDistance[i] + map[i][j]),表示到j点的最短距离等于当前到j点的最短距离与到i点的最短距离加上i点到j点的距离的最小值。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2),n为顶点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n^2),n为顶点数。
1 | private static int dp(int start, int end) { |
方法二:BFS(广度优先搜索)
思路:BFS(广度优先搜索),从起点开始扩展直接可达的点,第一次扩展到终点的路径即最短路径,结束搜素。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),n为顶点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),n为顶点数。
1 | private static int bfs(int start, int end) { |
方法三:DFS(深度优先搜索)
思路:DFS(深度优先搜索),从起点开始递归(递归采用栈来实现)搜素直接可达的点,需要将所有到终点的路径全部搜素出来,取最优值即为最短路径。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),n为顶点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),n为顶点数。
1 | private static int dfs(int start, int end) { |
方法四:Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉算法)
思路:Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉算法,更适合求单源最短路径),每次寻找离起点距离最短的点,得到以该点为中间点到各顶点的距离,然后更新当前从起点到各顶点的最短距离,重复n(n为顶点个数)次。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2),n为顶点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),n为顶点数。
1 | private static int dijkstra(int start, int end) { |
方法五:Floyd(佛洛依德算法)
思路:Floyd(佛洛依德算法,经化简已类式动态规划,更适合求多源最短路径),遍历顶点,求出以遍历的顶点k为中间点的所有顶点i到顶点j的距离,如果这个距离比顶点i到顶点j的当前最短距离还短,则更新顶点i到顶点j最短距离。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n^3),n为顶点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n^2),n为顶点数。
1 | private static int floyd(int start, int end) { |
学习所得,资料、图片部分来源于网络,如有侵权,请联系本人删除。
才疏学浅,若有错误或不当之处,可批评指正,还请见谅!


